Search the Blog
Categories
- Books & Reading
- Broadband Buzz
- Census
- Education & Training
- General
- Grants
- Information Resources
- Library Management
- Nebraska Center for the Book
- Nebraska Memories
- Now hiring @ your library
- Preservation
- Pretty Sweet Tech
- Programming
- Public Library Boards of Trustees
- Public Relations
- Talking Book & Braille Service (TBBS)
- Technology
- Uncategorized
- What's Up Doc / Govdocs
- Youth Services
Archives
Subscribe
Author Archives: Mary Sauers
Friday Reads — Atlas : The Story of Pa Salt, by Lucinda Riley and Harry Whittaker
Earlier this year, I read and did a Friday Reads post about The Seven Sisters series by Lucinda Riley. Atlas : The Story of Pa Salt is the 8th book in that series, released in May of this year after a two-year gap, and let me tell you, it was worth the wait! Sadly, Lucinda Riley died of oesophageal cancer in 2021, and her son, Harry Whittaker, completed this final book in the series. And once again, it does not disappoint. Spanning a lifetime of love and loss, crossing borders and oceans, Atlas: The Story of Pa Salt, draws Lucinda Riley’s saga to its stunning, unforgettable conclusion. I listened to the audio version and was amazed at how masterfully all of the pieces of the seven previous books came together. I won’t say more, because to do so would give away too much, but trust me when I say–this book was a non-stop page-turner!
1928, Paris. A boy is found, moments from death, and taken in by a kindly family. Gentle, precocious, talented, he flourishes in his new home, and the family show him a life he hadn’t dreamed possible. But he refuses to speak a word about who he really is.
As he grows into a young man, falling in love and taking classes at the prestigious Conservatoire de Paris, he can almost forget the terrors of his past, or the promise he has vowed to keep. But across Europe an evil is rising, and no-one’s safety is certain. In his heart, he knows the time will come when he must flee once more.
2008, the Aegean. The seven sisters are gathered together for the first time, on board the Titan, to say a final goodbye to the enigmatic father they loved so dearly.
To the surprise of everyone, it is the missing sister who Pa Salt has chosen to entrust with the clue to their pasts. But for every truth revealed, another question emerges. The sisters must confront the idea that their adored father was someone they barely knew. And even more shockingly: that these long-buried secrets may still have consequences for them today. In this epic conclusion to the Seven Sisters series, everything will be revealed! [Audible]
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for March and April, 2023. Included are reports from the Nebraska Brand Committee, the Nebraska Department of Banking and Finance, the Nebraska Arts Council, the Nebraska Commission for the Blind and Visually Impaired, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
Book Briefs: New University of Nebraska Press Books at the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse
The Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse receives documents every month from all Nebraska state agencies, including the University of Nebraska Press (UNP). Each month we will be showcasing the UNP books that the Clearinghouse has received.
UNP books, as well as all Nebraska state documents, are available for checkout by libraries and librarians for their patrons.
Here are the UNP books the Clearinghouse received in March and April, 2023:
The Begging Question : Sweden’s Social Responses to the Roma Destitute, by Erik Hansson ; Series: Cultural Geographies + Rewriting the Earth
Begging, thought to be an inherently un-Swedish phenomenon, became a national fixture in the 2010s as homeless Romanian and Bulgarian Roma EU citizens arrived in Sweden seeking economic opportunity. People without shelter were forced to use public spaces as their private space, disturbing aesthetic and normative orders, creating anxiety among Swedish subjects and resulting in hate crimes and everyday racism.
Parallel with Europe’s refugee crisis in the 2010s, the “begging question” peaked. The presence of the media’s so-called EU migrants caused a crisis in Swedish society along political, juridical, moral, and social lines due to the contradiction embodied in the Swedish authorities’ denial of social support to them while simultaneously seeking to maintain the nation’s image as promoting welfare, equality, and antiracism.
In The Begging Question Erik Hansson argues that the material configurations of capitalism and class society are not only racialized but also unconsciously invested with collective anxieties and desires. By focusing on Swedish society’s response to the begging question, Hansson provides insight into the dialectics of racism. He shrewdly deploys Marxian economics and Lacanian psychoanalysis to explain how it became possible to do what once was thought impossible: criminalize begging and make fascism politically mainstream, in Sweden. What Hansson reveals is not just an insight into one of the most captivating countries on earth but also a timely glimpse into what it means to be human.
The Collected Writings of Sherman and Grace Coolidge, Edited by Tadeusz Lewandowski
Sherman and Grace Coolidge were a remarkable couple in many respects. Sherman Coolidge (Runs On Top), born in the early 1860s into the Northern band of Arapahos, experienced the extreme violence of the Indian Wars, including the death of his father, as a young boy. Grace Wetherbee Coolidge was born into wealth and privilege in 1873, only to reject her life as a New York heiress and become a missionary on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming. It was there that Sherman and Grace met and later married in 1902.
After eight years together at Wind River, both went on to achieve prominence: Sherman as the president of the Native-run reform group the Society of American Indians (1911–1923), Grace as the author of Teepee Neighbors, a book describing her time on the reservation that drew praise from critics such as H. L. Mencken. Sherman was an Episcopal priest and a mesmerizing speaker who had the unique ability to blend his assimilated Western perspective with Arapaho values to educate the American public about the significant challenges facing Native peoples, including endemic poverty, racism, and inequality. Offering unprecedented entrée into the most significant writings and documents of a leading Native American advocate and his wife, this volume is an intimate portrait of their life and contributes to our understanding of American Indian activism at a key moment of Indigenous resurgence against the settler state.
Empire Between the Lines : Imperial Culture in British and French Trench Newspapers of the Great War ; by Elizabeth Stice. Series: Studies in War, Society, and the Military
Although the Great War was sparked and fueled by nationalism, it was ultimately a struggle between empires. The shots fired in Sarajevo mobilized citizens and subjects across far-flung continents that were connected by European empires. This imperial experience of the Great War influenced European soldiers’ ideas about the conflict, leading them to reimagine empires and their places with them and eventually reshaping imperial cultures.
In Empire between the Lines Elizabeth Stice analyzes stories, poetry, plays, and cartoons in British and French trench newspapers to demonstrate how British and French soldiers experienced and envisioned empires through the war and the war through empire. By establishing the imperial context for European soldiers and exploring representations of colonial troops, depictions of non-European campaigns, and descriptions of the German enemy, Stice argues that while certain narratives from prewar imperial culture persisted, the experience of the war also created new, competing narratives about empire and colonized peoples.
Empire between the Lines is the first study of its kind to consult British and French newspapers together, offering an innovative lens for viewing the public discourse of the trenches. By interrogating the relationship between British and French soldiers and empire during the war, Stice increases our understanding of the worldview of ordinary men in extraordinary times.
The First Atomic Bomb : the Trinity Site in New Mexico, by Janet Farrell Brodie. Series: America’s Public Lands
On July 16, 1945, just weeks before the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki that brought about the surrender of Japan and the end of World War II, the United States unleashed the world’s first atomic bomb at the Trinity testing site located in the remote Tularosa Valley in south-central New Mexico. Immensely more powerful than any weapon the world had seen, the bomb’s effects on the surrounding and downwind communities of plants, animals, birds, and humans have lasted decades.
In The First Atomic Bomb Janet Farrell Brodie explores the history of the Trinity test and those whose contributions have rarely, if ever, been discussed—the men and women who constructed, served, and witnessed the first test—as well as the downwinders who suffered the consequences of the radiation. Concentrating on these ordinary people, laborers, ranchers, and Indigenous peoples who lived in the region and participated in the testing, Brodie corrects the lack of coverage in existing scholarship on the essential details and everyday experiences of this globally significant event. The First Atomic Bomb also covers the environmental preservation of the Trinity test site and compares it with the wide range of atomic sites now preserved independently or as part of the new Manhattan Project National Historical Park. Although the Trinity site became a significant node for testing the new weapons of the postwar United States, it is known today as an officially designated National Historic Landmark. Brodie presents a timely, important, and innovative study of an explosion that carries special historical weight in American memory.
The Forgotten Diaspora : Mesoamerican Migrations and the Making of the U.S.-Mexico Borderlands, by Travis Jeffres. Series: Borderlands and Transcultural Studies
In The Forgotten Diaspora Travis Jeffres explores how Native Mexicans involved in the conquest of the Greater Southwest pursued hidden agendas, deploying a covert agency that enabled them to reconstruct Indigenous communities and retain key components of their identities even as they were technically allied with and subordinate to Spaniards. Resisting, modifying, and even flatly ignoring Spanish directives, Indigenous Mexicans in diaspora co-created the U.S.-Mexico borderlands and laid enduring claims to the region.
Jeffres contends that tens of thousands—perhaps hundreds of thousands—of central Mexican Natives were indispensable to Spanish colonial expansion in the Greater Southwest in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. These vital allies populated frontier settlements, assisted in converting local Indians to Christianity, and provided essential labor in the mining industry that drove frontier expansion and catapulted Spain to global hegemony. However, Nahuatl records reveal that Indigenous migrants were no mere auxiliaries to European colonial causes; they also subverted imperial aims and pursued their own agendas, wresting lands, privileges, and even rights to self-rule from the Spanish Crown. Via Nahuatl-language “hidden transcripts” of Native allies’ motivations and agendas, The Forgotten Diaspora reimagines this critical yet neglected component of the hemispheric colonial-era scattering of the Americas’ Indigenous peoples.
From the Boarding Schools : Apache Indian Students Speak, by Arnold Krupat
Arnold Krupat’s From the Boarding Schools makes available previously unheard Apache voices from the Indian boarding schools. It includes selections from two unpublished autobiographies by Sam Kenoi and Dan Nicholas, produced in the 1930s with the anthropologist Morris Opler, as well as material by and about Vincent Natalish, a contemporary of Kenoi and Nicholas.
Natalish was one of more than one hundred Apaches taken from Fort Marion to the Carlisle Indian School by its superintendent, Captain Richard Henry Pratt, in 1887. A considerable number of these students died at the school, and many who were sent home for illness or poor health did not recover. Natalish, however, remained at Carlisle and graduated in 1899. He married, had a son, and lived and worked in New York. He also actively sought the release of his relatives and other Apaches held prisoner at Fort Sill, Oklahoma.
Apache people have been telling and circulating stories among themselves for generations. But in contrast to their neighbors the Hopis and the Navajos, Apaches have produced relatively few written autobiographical narratives, and even fewer about their boarding school experiences. Supplementing the narratives with detailed cultural and historical commentary, From the Boarding Schools brings these lived experiences from the archives into current discourse.
The Indigenous Paleolithic of the Western Hemisphere, by Paulette F.C. Steeves
2022 Choice Outstanding Academic Title
The Indigenous Paleolithic of the Western Hemisphere is a reclaimed history of the deep past of Indigenous people in North and South America during the Paleolithic. Paulette F. C. Steeves mines evidence from archaeology sites and Paleolithic environments, landscapes, and mammalian and human migrations to make the case that people have been in the Western Hemisphere not only just prior to Clovis sites (10,200 years ago) but for more than 60,000 years, and likely more than 100,000 years.
Steeves discusses the political history of American anthropology to focus on why pre-Clovis sites have been dismissed by the field for nearly a century. She explores supporting evidence from genetics and linguistic anthropology regarding First Peoples and time frames of early migrations. Additionally, she highlights the work and struggles faced by a small yet vibrant group of American and European archaeologists who have excavated and reported on numerous pre-Clovis archaeology sites.
In this first book on Paleolithic archaeology of the Americas written from an Indigenous perspective, The Indigenous Paleolithic of the Western Hemisphere includes Indigenous oral traditions, archaeological evidence, and a critical and decolonizing discussion of the development of archaeology in the Americas.
Losing Eden : An Environmental History of the American West, by Sara Dant. New Edition. Series: Environment and Region in the American West
Historical narratives often concentrate on wars and politics while omitting the central role and influence of the physical stage on which history is carried out. In Losing Eden award-winning historian Sara Dant debunks the myth of the American West as “Eden” and instead embraces a more realistic and complex understanding of a region that has been inhabited and altered by people for tens of thousands of years.
In this lively narrative Dant discusses the key events and topics in the environmental history of the American West, from the Beringia migration, Columbian Exchange, and federal territorial acquisition to post–World War II expansion, resource exploitation, and current climate change issues. Losing Eden is structured around three important themes: balancing economic success and ecological destruction, creating and protecting public lands, and achieving sustainability.
This revised and updated edition incorporates the latest science and thinking. It also features a new chapter on climate change in the American West, a larger reflection on the region’s multicultural history, updated current events, expanded and diversified suggested readings, along with new maps and illustrations. Cohesive and compelling, Losing Eden recognizes the central role of the natural world in the history of the American West and provides important analysis on the continually evolving relationship between the land and its inhabitants.
Mud, Blood, and Ghosts : Populism, Eugenics, and Spiritualism in the American West, by Julie Carr
Populism has become a global movement associated with nationalism and strong-man politicians, but its root causes remain elusive. Mud, Blood, and Ghosts exposes one deep root in the soil of the American Great Plains. Julie Carr traces her own family’s history through archival documents to draw connections between U.S. agrarian populism, spiritualism, and eugenics, helping readers to understand populism’s tendency toward racism and exclusion.
Carr follows the story of her great-grandfather Omer Madison Kem, three-term Populist representative from Nebraska, avid spiritualist, and committed eugenicist, to explore persistent themes in U.S. history: property, personhood, exclusion, and belonging. While recent books have taken seriously the experiences of poor whites in rural America, they haven’t traced the story to its origins. Carr connects Kem’s journey with that of America’s white establishment and its fury of nativism in the 1920s. Presenting crucial narratives of Indigenous resistance, interracial alliance and betrayal, radical feminism, lifelong hauntings, land policy, debt, shame, grief, and avarice from the Gilded Age through the Progressive Era, Carr asks whether we can embrace the Populists’ profound hopes for a just economy while rejecting the barriers they set up around who was considered fully human, fully worthy of this dreamed society.
Recovering Women’s Past : New Epistemologies, New Ventures, Edited by Severine Genieys-Kirk. Series: Women and Gender in the Early Modern World
Feminist rewriting of history is designed not merely to reshape our collective memory and collective imaginary but also to challenge deeply ingrained paradigms about knowledge production. This feminist rewriting raises important questions for early modern scholars, especially in bringing to life the works of our foremothers and in reconsidering women’s agency.
Recovering Women’s Past, edited by Séverine Genieys-Kirk, is a collection of essays that focus on how women born before the nineteenth century have claimed a place in history and how they have been represented in the collective memory from the Renaissance to the twenty-first century. Scrutinizing the legacies of such politically minded women as Catherine de’ Medici, Queen Isabella of Castile, Emilie du Châtelet, and Olympe de Gouges, the volume’s contributors reflect on how our histories of women (in philosophy, literature, history, and the visual and performative arts) have been shaped by the discourses of their representation, how these discourses have been challenged, and how they can be reassessed both within and beyond the confines of academia. Recovering Women’s Past disseminates a more accurate, vital history of women’s past to engage in more creative and artistic encounters with our intellectual foremothers by creating imaginative modes of representing new knowledge. Only in these interactions will we be able to break away from the prevailing stereotypes about women’s roles and potential and advance the future of feminism.
Without Warning : The Tornado of Udall, Kansas, by Jim Minick
In 1955 the small town of Udall, Kansas, was home to oil field workers, homemakers, and teenagers looking ahead to their futures. But on the night of May 25, an F5 tornado struck their town without warning. In three minutes the tornado destroyed most of the buildings, including the new high school. It toppled the water tower. It lifted a pickup truck, stripped off its cab, and hung the frame in a tree. By the time the tornado moved on, it had killed 82 people and injured 270 others, more than half the town’s population of roughly 600 people. It remains the deadliest tornado in the history of Kansas.
Jim Minick’s nonfiction account, Without Warning, tells the human story of this disaster, moment by moment, from the perspectives of those who survived. His spellbinding narrative connects this history to our world today. Minick demonstrates that even if we have never experienced a tornado, we are still a people shaped and defined by weather and the events that unfold in our changing climate. Through the tragedy and hope found in this story of destruction, Without Warning tells a larger story of community, survival, and how we might find our way through the challenges of the future.
**Pictures and Synopses courtesy of University of Nebraska Press.
Friday Reads : The Seven Sisters, by Lucinda Riley
Some of you may already know about, and have read this series, but I just recently discovered The Seven Sisters, by Lucinda Riley, and I’m amazed I didn’t know about it sooner. There are currently seven books in the series, one for each sister, whose names are based on the star cluster named the Seven Sisters of the Pleiades in Greek mythology. An eighth and final book is due out in May of this year, telling the story of their adoptive father, Pa Salt.
I have to tell you, I was hooked from the very first book, and am currently listening to and reading book seven. Each sister, her talent, and her story has a connection to a unique person, thing, and piece of history, from all over the world.
Book 1– The Seven Sisters: Maia D’Aplièse and her five sisters gather together at their childhood home–a fabulous, secluded castle situated on the shores of Lake Geneva–having been told that their beloved adoptive father, the elusive billionaire they call Pa Salt, has died.
Each of them is handed a tantalising clue to their true heritage–a clue which takes Maia across the world to a crumbling mansion in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil . . .
Eighty years earlier, in the Belle Époque of Rio, 1927, Izabela Bonifacio’s father has aspirations for his daughter to marry into aristocracy. But Izabela longs for adventure, and convinces him to allow her to accompany the family of a renowned architect on a trip to Paris. In the heady, vibrant streets of Montparnasse, she meets ambitious young sculptor Laurent Brouilly, and knows at once that her life will never be the same again.
Book 2–The Storm Sister: Ally D’Aplièse is about to compete in one of the world’s most perilous yacht races, when she hears the news of her adoptive father’s sudden, mysterious death. Rushing back to meet her five sisters at their family home, she discovers that her father—an elusive billionaire affectionately known to his daughters as Pa Salt—has left each of them a tantalising clue to their true heritage.
Ally has also recently embarked on a deeply passionate love affair that will change her destiny forever. But with her life now turned upside down, Ally decides to leave the open seas and follow the trail that her father left her, which leads her to the icy beauty of Norway….
There, Ally begins to discover her roots—and how her story is inextricably bound to that of a young unknown singer, Anna Landvik, who lived there over a hundred years before and sang in the first performance of Grieg’s iconic music set to Ibsen’s play Peer Gynt. As Ally learns more about Anna, she also begins to question who her father, Pa Salt, really was. And why is the seventh sister missing?
Book 3– The Shadow Sister: Star D’Aplièse is at a crossroads in her life after the sudden death of her beloved father – the elusive billionaire, named Pa Salt by his six daughters, all adopted by him from the four corners of the world. He has left each of them a clue to their true heritage, but Star – the most enigmatic of the sisters – is hesitant to step out of the safety of the close relationship she shares with her sister CeCe. In desperation, she decides to follow the first clue she has been left, which leads her to an antiquarian bookshop in London, and the start of a whole new world…
A hundred years earlier, headstrong and independent Flora MacNichol vows she will never marry. She is happy and secure in her home in the Lake District, living close to her idol, Beatrix Potter, when machinations outside of her control lead her to London, and the home of one of Edwardian society’s most notorious players, Alice Keppel. Flora is pulled between passionate love and duty to her family, but finds herself a pawn in a game – the rules of which are only known to others, until a meeting with a mysterious gentleman unveils the answers that Flora has been searching for her whole life…
As Star learns more of Flora’s incredible journey, she too goes on a voyage of discovery, finally stepping out of the shadow of her sister and opening herself up to the possibility of love.
Book 4–The Pearl Sister: CeCe D’Aplièse has always felt like an outcast. But following the death of her father—the reclusive billionaire affectionately called Pa Salt by the six daughters he adopted from around the globe—she finds herself more alone than ever. With nothing left to lose, CeCe delves into the mystery of her origins. The only clues she holds are a black and white photograph and the name of a female pioneer who once lived in Australia.
One hundred years earlier, Kitty McBride, a Scottish clergyman’s daughter, abandons her conservative upbringing to serve as the companion to a wealthy woman traveling from Edinburgh to Adelaide. Her ticket to a new land brings the adventure she dreamed of and a love that she had never imagined.
When CeCe herself finally reaches the searing heat and dusty plains of the Red Centre of Australia, something deep within her responds to the energy of the area and the ancient culture of the Aboriginal people. As she comes closer to finding the truth of her ancestry, CeCe begins to believe that this untamed, vast continent could offer her what she never thought possible: a sense of belonging, and a home.
Book 5–The Moon Sister: After the death of her father – Pa Salt, an elusive billionaire who adopted his six daughters from around the globe – Tiggy D’Aplièse, trusting her instincts, moves to the remote wilds of Scotland. There she takes a job doing what she loves: caring for animals on the vast and isolated Kinnaird estate, employed by the enigmatic and troubled Laird, Charlie Kinnaird.
Her decision alters her future irrevocably when Chilly, an ancient gypsy who has lived for years on the estate, tells her that not only does she possess a sixth sense, passed down from her ancestors, but it was foretold long ago that he would be the one to send her back home to Granada in Spain.
In the shadow of the magnificent Alhambra, Tiggy discovers her connection to the fabled gypsy community of Sacromonte, who were forced to flee their homes during the civil war, and to ‘La Candela’, the greatest flamenco dancer of her generation. From the Scottish Highlands and Spain to South America and New York, Tiggy follows the trail back to her own exotic but complex past. And under the watchful eye of a gifted gypsy bruja, she begins to embrace her own talent for healing.
But when fate takes a hand, Tiggy must decide whether to stay with her newfound family or return to Kinnaird and Charlie….
Book 6–The Sun Sister: To the outside world, Electra D’Aplièse seems to be the woman with everything: as one of the world’s top models, she is beautiful, rich and famous.
Yet beneath the veneer, Electra’s already tenuous control over her state of mind has been rocked by the death of her father, Pa Salt, the elusive billionaire who adopted his six daughters from across the globe. Struggling to cope, she turns to alcohol and drugs. As those around her fear for her health, Electra receives a letter from a complete stranger who claims to be her grandmother.
In 1939, Cecily Huntley-Morgan arrives in Kenya from New York to nurse a broken heart. Staying with her godmother, a member of the infamous Happy Valley set, on the shores of beautiful Lake Naivasha, she meets Bill Forsythe, a notorious bachelor and cattle farmer with close connections to the proud Maasai tribe. But after a shocking discovery and with war looming, Cecily has few options. Moving up into the Wanjohi Valley, she is isolated and alone. Until she meets a young woman in the woods and makes her a promise that will change the course of her life for ever.
Sweeping from Manhattan to the magnificent wide-open plains of Africa, The Sun Sister is the sixth instalment in Lucinda Riley’s multi-million selling epic series, The Seven Sisters.
Book 7–The Missing Sister: They’ll search the world to find her. The six D’Aplièse sisters have each been on their own incredible journey to discover their heritage, but they still have one question left unanswered: who and where is the seventh sister?
They only have one clue – an image of a star-shaped emerald ring. The search to find the missing sister will take them across the globe – from New Zealand to Canada, England, France and Ireland – uniting them all in their mission to complete their family at last.
In doing so, they will slowly unearth a story of love, strength and sacrifice that began almost 100 years ago, as other brave young women risk everything to change the world around them.
Each book is so well written, and each voice performed so well, that I felt like I was really in each sister’s history and location. I’m excited to finish Book 7, and can’t wait for Book 8: Atlas, the Story of Pa Salt. Synopses courtesy of Audible.com and Amazon.com
Posted in Books & Reading, General, Information Resources
Tagged Book Covers, books, Friday Reads, Reading
Leave a comment
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for January and February, 2023. Included are reports from the Nebraska Department of Agriculture, the Nebraska Courts System, the Nebraska Game & Parks Commission, the Nebraska Department of Labor, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
Book Briefs: New University of Nebraska Press Books at the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse
The Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse receives documents every month from all Nebraska state agencies, including the University of Nebraska Press (UNP). Each month we will be showcasing the UNP books that the Clearinghouse has received.
UNP books, as well as all Nebraska state documents, are available for checkout by libraries and librarians for their patrons.
Here are the UNP books the Clearinghouse received in January and February, 2023:
A Concise Dictionary of Nakoda (Assiniboine) by Vincent Collette; Series: Studies in the Native Languages of the Americas
A Concise Dictionary of Nakoda (Assiniboine) brings to life the hopes and dreams of Nakoda (Assiniboine) elders. The Nakoda language—also known as Assiniboine, an Ojibwe ethnonym meaning “Stone Enemy”—is an endangered Siouan language of the Mississippi Valley branch spoken in southern Saskatchewan and northern Montana. Nakoda belongs to the Dakotan dialectal continuum, which includes Dakota, Lakota, and Stoney.
The fieldwork for this project was done between 2018 and 2020 with Elder Wilma Kennedy, one of the last fluent speakers living in Carry The Kettle, Saskatchewan. The volume brings together many valuable stories and colorful expressions as well as archaic words that do not appear in any known sources of the language. Particular care was taken to obtain the derivatives of many verbal stems, along with sentences for many of the verbs, adverbs, and other function words.
More than a list of words, this volume contains definitions and standard spellings along with a wealth of grammatical information. The dictionary contains more than 6,000 Nakoda-to-English translations, more than 3,000 English-to-Nakoda translations, and more than 1,500 sentences that will be extremely helpful for those interested in mastering the different usages of words and the various sentence patterns of the language. This dictionary of Nakoda can be used by anyone interested in learning or would like to refresh their knowledge of the language.
A Maverick Boasian : The Life and Work of Alexander A Goldenweiser by Sergei Kan; Series: Critical Studies in the History of Anthropology
A Maverick Boasian explores the often contradictory life of Alexander Goldenweiser (1880–1940), a scholar considered by his contemporaries to be Franz Boas’s most brilliant and most favored student. The story of his life and scholarship is complex and exciting as well as frustrating. Although Goldenweiser came to the United States from Russia as a young man, he spent the next forty years thinking of himself as a European intellectual who never felt entirely at home. A talented ethnographer, he developed excellent rapport with his Native American consultants but cut short his fieldwork due to lack of funds. An individualist and an anarchist in politics, he deeply resented having to compromise any of his ideas and freedoms for the sake of professional success. A charming man, he risked his career and family life to satisfy immediate needs and wants.
A number of his books and papers on the relationship between anthropology and other social sciences helped foster an important interdisciplinary conversation that continued for decades after his death. For the first time, Sergei Kan brings together and examines all of Goldenweiser’s published scholarly works, archival records, personal correspondences, nonacademic publications, and living memories from several of Goldenweiser’s descendants.
Goldenweiser attracted attention for his unique progressive views on such issues as race, antisemitism, immigration, education, pacifism, gender, and individual rights. His was a major voice in a chorus of progressive Boasians who applied the insights of their discipline to a variety of questions on the American public’s mind. Many of the battles he fought are still with us today.
Aquaman and the War Against Oceans by Ryan Poll; Series: Encapsulations: Critical Comics Studies
The reimagining of Aquaman in The New 52 transformed the character from a joke to an important figure of ecological justice. In Aquaman and the War against Oceans, Ryan Poll argues that in this twenty-first-century iteration, Aquaman becomes an accessible figure for charting environmental violences endemic to global capitalism and for developing a progressive and popular ecological imagination.
Poll contends that The New 52 Aquaman should be read as an allegory that responds to the crises of the Anthropocene, in which the oceans have become sites of warfare and mass death. The Aquaman series, which works to bridge the terrestrial and watery worlds, can be understood as a form of comics activism by its visualizing and verbalizing how the oceans are beyond the projects of the “human” and “humanism” and, simultaneously, are all-too-human geographies that are inextricable from the violent structures of capitalism, white supremacy, and patriarchy. The New 52 Aquaman, Poll demonstrates, proves an important form of ocean literacy in particular and ecological literacy more generally.
Black Gun, Silver Star : the Life and Legend of Frontier Marshal Bass Reeves, New edition, by Art T. Burton
In The Story of Oklahoma, Deputy U.S. Marshal Bass Reeves appears as the “most feared U.S. marshal in the Indian country.” That Reeves was also an African American who had spent his early life enslaved in Arkansas and Texas made his accomplishments all the more remarkable. Black Gun, Silver Star sifts through fact and legend to discover the truth about one of the most outstanding peace officers in late nineteenth-century America—and perhaps the greatest lawman of the Wild West era.
Bucking the odds (“I’m sorry, we didn’t keep Black people’s history,” a clerk at one of Oklahoma’s local historical societies answered one query), Art T. Burton traces Reeves from his days of slavery to his Civil War soldiering to his career as a deputy U.S. marshal out of Fort Smith, Arkansas, when he worked under “Hanging Judge” Isaac C. Parker. Fluent in Creek and other regional Native languages, physically powerful, skilled with firearms, and a master of disguise, Reeves was exceptionally adept at apprehending fugitives and outlaws and his exploits were legendary in Oklahoma and Arkansas.
In this new edition Burton traces Reeves’s presence in the national media of his day as well as his growing modern presence in popular media such as television, movies, comics, and video games.
Breaking the Silence : Anthology of Liberian Poetry edited by Patricia Jabbeh Wesley; Series: African Poetry Book
Breaking the Silence is the first comprehensive collection of literature from Liberia since before the nation’s independence. Patricia Jabbeh Wesley has gathered work from the 1800s to the present, including poets and emerging young writers exploring contemporary literary traditions with African and African diaspora poetry that transcends borders. In this collection, Liberia’s founding settlers wrestle with their identity as African free slaves in the homeland from which their ancestors were captured, and writers of the early twentieth and twenty-first centuries find themselves navigating a landscape at odds with itself.
From poets of Liberia’s past to young writers of the present, the contributors to this volume celebrate the beauty of their nation while mourning the devastation of a long, bloody civil war.
Dog on Fire by Terese Svoboda; Series: Flyover Fiction
Out of a Shakespearean-wild Midwest dust storm, a man rises. “Just a glimpse of him,” says his sister; “every inch of him,” says his guilt-filled lover. “Close your eyes,” says his nephew. “What about it?” asks his father. The cupboard is filled with lime Jell-O, and there are aliens, deadly kissing, and a restless, alcoholic mother who carries a gun. “Every family is this normal,” insists the narrator. “Whoever noticed my brother, with a family as normal as this?” the beleaguered sister asks. Against the smoky prairie horizon and despite his seizures, a brother builds a life. Imbued with melancholy cheer, Dog on Fire unfolds around a family’s turmoil, past loves, and a mysterious death.
Hydronarratives : water, Environmental Justice, and a Just Transition by Matthew S. Henry
The story of water in the United States is one of ecosystemic disruption and social injustice. From the Standing Rock Indian Reservation and Flint, Michigan, to the Appalachian coal and gas fields and the Gulf Coast, low-income communities, Indigenous communities, and communities of color face the disproportionate effects of floods, droughts, sea level rise, and water contamination.
In Hydronarratives Matthew S. Henry examines cultural representations that imagine a just transition, a concept rooted in the U.S. labor and environmental justice movements to describe an alternative economic paradigm predicated on sustainability, economic and social equity, and climate resilience. Focused on regions of water insecurity, from central Arizona to central Appalachia, Henry explores how writers, artists, and activists have creatively responded to intensifying water crises in the United States and argues that narrative and storytelling are critical to environmental and social justice advocacy. By drawing on a wide and comprehensive range of narrative texts, historical documentation, policy papers, and literary and cultural scholarship, Henry presents a timely project that examines the social movement, just transition, and the logic of the Green New Deal, in addition to contemporary visions of environmental justice.
Mine Mine Mine by Uhuru Portia Phalafala; Series: African Poetry Book
Mine Mine Mine is a personal narration of Uhuru Portia Phalafala’s family’s experience of the migrant labor system brought on by the gold mining industry in Johannesburg, South Africa. Using geopoetics to map geopolitics, Phalafala follows the death of her grandfather during a historic juncture in 2018, when a silicosis class action lawsuit against the mining industry in South Africa was settled in favor of the miners.
Phalafala ties the catastrophic effects of gold mining on the miners and the environment in Johannesburg to the destruction of Black lives, the institution of the Black family, and Black sociality. Her epic poem addresses racial capitalism, bringing together histories of the transatlantic and trans-Indian slave trades, of plantation economies, and of mining and prison-industrial complexes. As inheritor of the migrant labor lineage, she uses her experience to explore how Black women carry intergenerational trauma of racial capitalism in their bodies and intersects the personal and national, continental and diasporic narration of this history within a critical race framework.
Segregation Made Them Neighbors : an Archaeology of Racialization in Boise, Idaho by William A. White III; Series: Historical Archaeology of the American West
Segregation Made Them Neighbors investigates the relationship between whiteness and nonwhiteness through the lenses of landscapes and material culture. William A. White III uses data collected from a public archaeology and digital humanities project conducted in the River Street neighborhood in Boise, Idaho, to investigate the mechanisms used to divide local populations into racial categories. The River Street Neighborhood was a multiracial, multiethnic enclave in Boise that was inhabited by African American, European American, and Basque residents. Building on theoretical concepts from whiteness studies and critical race theory, this volume also explores the ways Boise’s residents crafted segregated landscapes between the 1890s and 1960s to establish white and nonwhite geographies.
White describes how housing, urban infrastructure, ethnicity, race, and employment served to delineate the River Street neighborhood into a nonwhite space, an activity that resulted in larger repercussions for other Boiseans. Using material culture excavated from the neighborhood, White describes how residents used mass-produced products to assert their humanity and subvert racial memes.
By describing the effects of racial discrimination, real-estate redlining, and urban renewal on the preservation of historic properties in the River Street neighborhood, Segregation Made Them Neighbors illustrates the symbiotic mechanisms that also prevent equity and representation through historic preservation in other cities in the American West.
Speculative Wests : Popular Representations of a Region and Genre by Michael K. Johnson; Series: Postwestern Horizons
Looking across the cultural landscape of the twenty-first century, its literature, film, television, comic books, and other media, we can see multiple examples of what Shelley S. Rees calls a “changeling western,” what others have called “weird westerns,” and what Michael K. Johnson refers to as “speculative westerns”—that is, hybrid western forms created by merging the western with one or more speculative genres or subgenres, including science fiction, fantasy, horror, and alternate history.
Speculative Wests investigates both speculative westerns and other speculative texts that feature western settings. Just as “western” refers both to a genre and a region, Johnson’s narrative involves a study of both genre and place, a study of the “speculative Wests” that have begun to emerge in contemporary texts such as the zombie-threatened California of Justina Ireland’s Deathless Divide (2020), the reimagined future Navajo nation of Rebecca Roanhorse’s Sixth World series (2018–19), and the complex temporal and geographic borderlands of Alfredo Véa’s time travel novel The Mexican Flyboy (2016). Focusing on literature, film, and television from 2016 to 2020, Speculative Wests creates new visions of the American West.
Two Open Doors in a Field by Sophie Klahr; Series: The Backwaters Prize in Poetry Honorable Mention
The poems of Two Open Doors in a Field are constructed through deliberate limitations, restlessly exploring place, desire, and spirituality. A profusion of sonnets rises from a single circumstance: Sophie Klahr’s experience of driving thousands of miles alone while listening to the radio, where unexpected landscapes make listening to the unexpected more acute. Accompanied by the radio, Klahr’s experience of land is transformed by listening, and conversely, the body of the radio is sometimes lost to the body of the land. The love story at the core of this work, Klahr’s bond with Nebraska, becomes the engine of this travelogue. However far the poems range beyond Nebraska, they are tethered to an environment of work and creation, a place of dirt beneath the nails where one can see every star and feel, acutely, the complexity of connection.
Women, Empires, and Body Politics at the United Nations, 1946-1975 by Giusi Russo; Series: Expanding Frontiers: Interdisciplinary Approaches to Studies of Women, Gender, and Sexuality
Women, Empires, and Body Politics at the United Nations, 1946–1975 tells the story of how women’s bodies were at the center of the international politics of women’s rights in the postwar period. Giusi Russo focuses on the United Nation Commission on the Status of Women and its multiple interactions with the colonial and postcolonial worlds, showing how—depending on the setting and the inquiry—liberal, imperial, and transnational feminisms could coexist.
Russo suggests that in the early stages of identifying discriminating agents in women’s lives, UN commissioners overlooked the nation-state and went through a process of fighting discrimination without identifying the discriminator. However, it was the focus on empire that allowed for a clear identification of how gender constructs were instrumental to state politics and the exclusion of women. An emphasis on colonial practices also generated a focus on the body and radically shifted the commission’s politics from formal equality to a gender-based equilibrium of rights that emphasized practice rather than law. Through a multidisciplinary approach, Russo looks at the women living under colonial and postcolonial systems as the key actors in defining the politics of women’s rights at the UN.
**Pictures and Synopses courtesy of University of Nebraska Press.
What’s Up Doc? 2022 State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

Below are the state agency publications that were received at the Nebraska Library Commission in 2022.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for November and December, 2022. Included are reports from the Nebraska Department of Corrections, the Nebraska Department of Criminal Justice, the Nebraska Legislature, the Nebraska Department of Transportation, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
Book Briefs: New University of Nebraska Press Books at the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse
The Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse receives documents every month from all Nebraska state agencies, including the University of Nebraska Press (UNP). Each month we will be showcasing the UNP books that the Clearinghouse has received.
UNP books, as well as all Nebraska state documents, are available for checkout by libraries and librarians for their patrons.
Here are the UNP books the Clearinghouse received in November and December, 2022:
Continental Reckoning : The American West in the Age of Expansion by Elliott West. Series: History of the American West
In Continental Reckoning renowned historian Elliott West presents a sweeping narrative of the American West and its vital role in the transformation of the nation. In the 1840s, by which time the United States had expanded to the Pacific, what would become the West was home to numerous vibrant Native cultures and vague claims by other nations. Thirty years later it was organized into states and territories and bound into the nation and world by an infrastructure of rails, telegraph wires, and roads and by a racial and ethnic order, with its Indigenous peoples largely dispossessed and confined to reservations.
Unprecedented exploration uncovered the West’s extraordinary resources, beginning with the discovery of gold in California within days of the United States acquiring the territory following the Mexican-American War. As those resources were developed, often by the most modern methods and through modern corporate enterprise, half of the contiguous United States was physically transformed. Continental Reckoning guides the reader through the rippling, multiplying changes wrought in the western half of the country, arguing that these changes should be given equal billing with the Civil War in this crucial transition of national life.
As the West was acquired, integrated into the nation, and made over physically and culturally, the United States shifted onto a course of accelerated economic growth, a racial reordering and redefinition of citizenship, engagement with global revolutions of science and technology, and invigorated involvement with the larger world. The creation of the West and the emergence of modern America were intimately related. Neither can be understood without the other. With masterful prose and a critical eye, West presents a fresh approach to the dawn of the American West, one of the most pivotal periods of American history.
Everywhen : Australia and the Language of Deep History by Ann McGrath, Laura Rademaker, and Jakelin Troy. Series: New Visions in Native American and Indigenous Studies
Everywhen is a groundbreaking collection about diverse ways of conceiving, knowing, and narrating time and deep history. Looking beyond the linear documentary past of Western or academic history, this collection asks how knowledge systems of Australia’s Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders can broaden our understandings of the past and of historical practice. Indigenous embodied practices for knowing, narrating, and reenacting the past in the present blur the distinctions of linear time, making all history now. Ultimately, questions of time and language are questions of Indigenous sovereignty. The Australian case is especially pertinent because Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people are among the few Native peoples without a treaty with their colonizers. Appreciating First Nations’ time concepts embedded in languages and practices, as Everywhen does, is a route to recognizing diverse forms of Indigenous sovereignties.
Everywhen makes three major contributions. The first is a concentration on language, both as a means of knowing and transmitting the past across generations and as a vital, albeit long-overlooked source material for historical investigation, to reveal how many Native people maintained and continue to maintain ancient traditions and identities through language. Everywhen also considers Indigenous practices of history, or knowing the past, that stretch back more than sixty thousand years; these Indigenous epistemologies might indeed challenge those of the academy. Finally, the volume explores ways of conceiving time across disciplinary boundaries and across cultures, revealing how the experience of time itself is mediated by embodied practices and disciplinary norms.
Everywhen brings Indigenous knowledges to bear on the study and meaning of the past and of history itself. It seeks to draw attention to every when, arguing that Native time concepts and practices are vital to understanding Native histories and, further, that they may offer a new framework for history as practiced in the Western academy.
Field Guide to a Hybrid Landscape : Photographs by Dana Fritz Photographs by Dana Fritz; Essays by Katie Anania, Rebecca Buller, and Rose-Marie Muzika; Maps by Salvador Lindquist.
In Field Guide to a Hybrid Landscape Dana Fritz traces the evolution of the Bessey Ranger District and Nursery of the Nebraska National Forest and Grasslands. Fritz’s contemporary photographs of this unique ecosystem, with provocative environmental essays, maps, and historical photographs from the U.S. Forest Service archives, illuminate the complex environmental and natural history of the site, especially as it relates to built environments, land use, and climate change.
The Nebraska National Forest at Halsey, as it is known colloquially, is the largest hand-planted forest in the Western Hemisphere, and formerly in the world. This hybrid landscape of a conifer forest overlaid onto a semiarid grassland just west of the one-hundredth meridian was an ambitious late nineteenth-century idea to create a timber industry, to reclaim a landscape considered disordered and unproductive, and to change the local climate in northcentral Nebraska. While the planners seemed not to appreciate the native grasslands that form the ecosystem of the Nebraska Sandhills, they did recognize the reliable water from the Dismal and Middle Loup Rivers that border the site. In 1902 the first federal nursery was established as part of the Dismal River Forest Reserve to produce seedlings for plains homesteads and the adjacent treeless tract of land. At that time tree planting was not used for carbon sequestration but to mitigate the wind and evaporation of moisture.
The Bessey Nursery now produces replacement seedlings for burned and beetle-damaged forests in the Rocky Mountains and for the Nebraska Conservation Trees Program. This constructed landscape of row-crop trees that were protected from fire for decades, yet never commercially harvested for timber, provides a rich metaphor for current environmental predicaments. The late nineteenth-century effort to reclaim with trees what was called the Great American Desert has evolved to a focus on twenty-first-century conservation, grassland restoration, and reforestation, all of which work to sequester carbon, maintain natural ecosystem balance, and mitigate large-scale climate change. Field Guide to a Hybrid Landscape offers a visual and critical examination of this unique managed landscape, which has implications far beyond its borders.
Franz Boas : Shaping Anthropology and Fostering Social Justice, by Rosemary Lévy Zumwalt. Series: Critical Studies in the History of Anthropology
Franz Boas defined the concept of cultural relativism and reoriented the humanities and social sciences away from race science toward an antiracist and anticolonialist understanding of human biology and culture. Franz Boas: Shaping Anthropology and Fostering Social Justice is the second volume in Rosemary Lévy Zumwalt’s two-part biography of the renowned anthropologist and public intellectual.
Zumwalt takes the reader through the most vital period in the development of Americanist anthropology and Boas’s rise to dominance in the subfields of cultural anthropology, physical anthropology, ethnography, and linguistics. Boas’s emergence as a prominent public intellectual, particularly his opposition to U.S. entry into World War I, reveals his struggle against the forces of nativism, racial hatred, ethnic chauvinism, scientific racism, and uncritical nationalism.
Boas was instrumental in the American cultural renaissance of the 1920s and 1930s, training students and influencing colleagues such as Melville Herskovits, Zora Neale Hurston, Benjamin Botkin, Alan Lomax, Langston Hughes, and others involved in combating racism and the flourishing Harlem Renaissance. He assisted German and European émigré intellectuals fleeing Nazi Germany to relocate in the United States and was instrumental in organizing the denunciation of Nazi racial science and American eugenics. At the end of his career Boas guided a network of former student anthropologists, who spread across the country to university departments, museums, and government agencies, imprinting his social science more broadly in the world of learned knowledge.
Franz Boas is a magisterial biography of Franz Boas and his influence in shaping not only anthropology but also the sciences, humanities, social science, visual and performing arts, and America’s public sphere during a period of great global upheaval and democratic and social struggle.
From Near and Far : A Transitional History of France, by Tyler Stovall. Series: France Overseas: Studies in Empire and Decolonization
From Near and Far relates the history of modern France from the French Revolution to the present. Noted historian Tyler Stovall considers how the history of France interacts with both the broader history of the world and the local histories of French communities, examining the impacts of Karl Marx, Ho Chi Minh, Paul Gauguin, and Josephine Baker alongside the rise of haute couture and the contemporary role of hip hop.
From Near and Far focuses on the interactions between France and three other parts of the world: Europe, the United States, and the French colonial empire. Taking this transnational approach to the history of modern France, Stovall shows how the theme of universalism, so central to modern French culture, has manifested itself in different ways over the last few centuries. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of narrative to French history, that historians tell the story of a nation and a people by bringing together a multitude of stories and tales that often go well beyond its boundaries. In telling these stories From Near and Far gives the reader a vision of France both global and local at the same time.
Gentry Rhetoric : Literacies, Letters, and Writing in an Elizabethan Community by Danial Ellis. Series: Early Modern Cultural Studies
Gentry Rhetoric examines the full range of influences on the Elizabethan and Jacobean genteel classes’ practice of English rhetoric in daily life. Daniel Ellis surveys how the gentry of late sixteenth- and early seventeenth-century Norfolk wrote to and negotiated with each other by employing Renaissance humanist rhetoric, both to solidify their identity and authority in resisting absolutism and authoritarianism, and to transform the political and social state. The rhetorical training that formed the basis of their formal education was one obvious influence. Yet to focus on this training exclusively allows only a limited understanding of the way this class developed the strategies that enabled them to negotiate, argue, and conciliate with one another to such an extent that they could both form themselves as a coherent entity and become the primary shapers of written English’s style, arrangement, and invention.
Gentry Rhetoric deeply and inductively examines archival materials in which members of the gentry discuss, debate, and negotiate matters relating to their class interests and political aspirations. Humanist rhetoric provided the bedrock of address, argumentation, and negotiation that allowed the gentry to instigate a political and educational revolution in seventeenth- and eighteenth-century England.
Keorapetse Kgositsile : Collected Poems, 1969-2018 by Keorapetse Kgositsile; Edited and with an introduction by Phillippa Yaa de Villiers and Uhuru Portia Phalafala. Series: African Poetry Book
Keorapetse Kgositsile, South Africa’s second poet laureate, was a political activist, teacher, and poet. He lived, wrote, and taught in the United States for a significant part of his life and collaborated with many influential and highly regarded writers, including Gwendolyn Brooks, Sterling Plumpp, Dudley Randall, and George Kent. This comprehensive collection of Kgositsile’s new and collected works spans almost fifty years.
During his lifetime, Kgositsile dedicated the majority of his poems to people or movements, documenting the struggle against racism, Western imperialism, and racial capitalism, and celebrating human creativity, particularly music, as an inherent and essential aspect of the global liberation struggle. This collection demonstrates the commitment to equality, justice, and egalitarianism fostered by cultural workers within the mass liberation movement. As the introduction notes, Kgositsile had an “undisputed ability to honor the truth in all its complexity, with a musicality that draws on the repository of memory and history, rebuilt through the rhythms and cadences of jazz.” Addressing themes of Black solidarity, displacement, and anticolonialism, Kgositsile’s prose is fiery, witty, and filled with conviction. This collection showcases a voice that wanted to change the world—and did.
Restoring Nature : the Evolution of Channel Islands National Park by Lary M. Dilsaver and Timothy J. Babalis. Series: America’s Public Lands
Off the coast of California, running from Santa Barbara to La Jolla, lies an archipelago of eight islands known as the California Channel Islands. The northern five were designated as Channel Islands National Park in 1980 to protect and restore the rich habitat of the islands and surrounding waters.
In the years since, that mission intensified as scientists discovered the extent of damage to the delicate habitats of these small fragments of land and to the surprisingly threatened sea around them. In Restoring Nature Lary M. Dilsaver and Timothy J. Babalis examine how the National Park Service has attempted to reestablish native wildlife and vegetation to the five islands through restorative ecology and public land management. The Channel Islands staff were innovators of the inventory and monitoring program whereby the resource problems were exposed. This program became a blueprint for management throughout the U.S. park system.
Dilsaver and Babalis present an innovative regional and environmental history of a little-known corner of the Pacific West, as well as a larger national narrative about how the Park Service developed its approach to restoration ecology, which became a template for broader Park Service policies that shaped the next generation of environmental conservation.
Sex, Gender, and Illegitimacy in the Castilian Noble Family, 1400-1600 by Grace E. Coolidge. Series: Women and Gender in the Early Modern World
Sex, Gender, and Illegitimacy in the Castilian Noble Family, 1400–1600 looks at illegitimacy across the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries and analyzes its implications for gender and family structure in the Spanish nobility, a class whose actions, structure, and power had immense implications for the future of the country and empire. Grace E. Coolidge demonstrates that women and men were able to challenge traditional honor codes, repair damaged reputations, and manipulate ideals of marriage and sexuality to encompass extramarital sexuality and the nearly constant presence of illegitimate children.
This flexibility and creativity in their sexual lives enabled members of the nobility to repair, strengthen, and maintain their otherwise fragile concept of dynasty and lineage, using illegitimate children and their mothers to successfully project the noble dynasty into the future—even in an age of rampant infant mortality that contributed to the frequent absence of male heirs. While benefiting the nobility as a whole, the presence of illegitimate children could also be disruptive to the inheritance process, and the entire system privileged noblemen and their aims and goals over the lives of women and children.
This book enriches our understanding of the complex households and families of the Spanish nobility, challenging traditional images of a strict patriarchal system by uncovering the hidden lives that made that system function.
Taking the Field : Soldiers, Nature, and Empire on American Frontiers by Amy Kohout. Series: Many Wests
Published in Cooperation with the William P. Clements Center for Southwest Studies, Southern Methodist University.
In the late nineteenth century, at a time when Americans were becoming more removed from nature than ever before, U.S. soldiers were uniquely positioned to understand and construct nature’s ongoing significance for their work and for the nation as a whole. American ideas and debates about nature evolved alongside discussions about the meaning of frontiers, about what kind of empire the United States should have, and about what it meant to be modern or to make “progress.” Soldiers stationed in the field were at the center of these debates, and military action in the expanding empire brought new environments into play.
In Taking the Field Amy Kohout draws on the experiences of U.S. soldiers in both the Indian Wars and the Philippine-American War to explore the interconnected ideas about nature and empire circulating at the time. By tracking the variety of ways American soldiers interacted with the natural world, Kohout argues that soldiers, through their words and their work, shaped Progressive Era ideas about both American and Philippine environments. Studying soldiers on multiple frontiers allows Kohout to inject a transnational perspective into the environmental history of the Progressive Era, and an environmental perspective into the period’s transnational history. Kohout shows us how soldiers—through their writing, their labor, and all that they collected—played a critical role in shaping American ideas about both nature and empire, ideas that persist to the present.
The Camp Fire Girls : Gender, Race, and American Girlhood, 1910–1980 by Jennifer Helgren. Series: Expanding Frontiers: Interdisciplinary Approaches to Studies of Women, Gender, and Sexuality
As the twentieth century dawned, progressive educators established a national organization for adolescent girls to combat what they believed to be a crisis of girls’ education. A corollary to the Boy Scouts of America, founded just a few years earlier, the Camp Fire Girls became America’s first and, for two decades, most popular girls’ organization. Based on Protestant middle-class ideals—a regulatory model that reinforced hygiene, habit formation, hard work, and the idea that women related to the nation through service—the Camp Fire Girls invented new concepts of American girlhood by inviting disabled girls, Black girls, immigrants, and Native Americans to join. Though this often meant a false sense of cultural universality, in the girls’ own hands membership was often profoundly empowering and provided marginalized girls spaces to explore the meaning of their own cultures in relation to changes taking place in twentieth-century America.
Through the lens of the Camp Fire Girls, Jennifer Helgren traces the changing meanings of girls’ citizenship in the cultural context of the twentieth century. Drawing on girls’ scrapbooks, photographs, letters, and oral history interviews, in addition to adult voices in organization publications and speeches, The Camp Fire Girls explores critical intersections of gender, race, class, nation, and disability.
The Complete Letters of Henry James, 1887-1888, Volume 1 by Henry James; Edited by Michael Anesko and Greg W. Zacharias; Katie Sommer, Associate Editor; With an introduction by Sarah Wadsworth. Series: The Complete Letters of Henry James
This first volume in The Complete Letters of Henry James, 1887–1888 contains 154 letters, of which 94 are published for the first time, written from early January to December 22, 1887. These letters mark Henry James’s ongoing efforts to care for his sister, develop his work, strengthen his professional status, build friendships, engage timely political and economic issues, and maximize his income. James details work on “The Aspern Papers,” Partial Portraits, and plans The Reverberator. This volume opens with James in the midst of a long sojourn in Italy and concludes with his inquiring about both the status of his essay to the American Copyright League and also the story “The Liar.”
The Dakota Way of Life by Ella Cara Deloria; Edited by Raymond J. DeMallie and Thierry Veyrié; Afterword by Philip J. Deloria. Series: Studies in the Anthropology of North American Indians
Ella Cara Deloria devoted much of her life to the study of the language and culture of the Sioux (Dakota and Lakota). The Dakota Way of Life is the result of the long history of her ethnographic descriptions of traditional Dakota culture and social life. Deloria was the most prolific Native scholar of the greater Sioux Nation, and the results of her work comprise an essential source for the study of the greater Sioux Nation culture and language. For years she collected material for a study that would document the variations from group to group. Tragically, her manuscript was not published during her lifetime, and at the end of her life all of her major works remained unpublished.
Deloria was a perfectionist who worked slowly and cautiously, attempting to be as objective as possible and revising multiple times. As a result, her work is invaluable. Her detailed cultural descriptions were intended less for purposes of cultural preservation than for practical application. Deloria was a scholar through and through, and yet she never let her dedication to scholarship overwhelm her sense of responsibility as a Dakota woman, with family concerns taking precedence over work. Her constant goal was to be an interpreter of an American Indian reality to others. Her studies of the Sioux are a monument to her talent and industry.
The Imperial Gridiron : Manhood, Civilization, and Football at the Carlisle Indian Industrial School by Matthew Bentley and John Bloom.
The Imperial Gridiron examines the competing versions of manhood at the Carlisle Indian Industrial School between 1879 and 1918. Students often arrived at Carlisle already engrained with Indigenous ideals of masculinity. On many occasions these ideals would come into conflict with the models of manhood created by the school’s original superintendent, Richard Henry Pratt. Pratt believed that Native Americans required the “embrace of civilization,” and he emphasized the qualities of self-control, Christian ethics, and retaliatory masculinity. He encouraged sportsmanship and fair play over victory.
Pratt’s successors, however, adopted a different approach, and victory was enshrined as the main objective of Carlisle sports. As major stars like Jim Thorpe and Lewis Tewanima came to the fore, this change in approach created a conflict over manhood within the school: should the competitive athletic model be promoted, or should Carlisle focus on the more self-controlled, Christian ideal as promoted by the school’s Young Men’s Christian Association? The answer came from the 1914 congressional investigation of Carlisle. After this grueling investigation, Carlisle’s model of manhood starkly reverted to the form of the Pratt years, and by the time the school closed in 1918, the school’s standards of masculinity had come full circle.
**Pictures and Synopses courtesy of University of Nebraska Press.
Friday Reads: The Personal Librarian
The Personal Librarian is a remarkable novel about J. P. Morgan’s personal librarian, Belle da Costa Greene, the Black American woman who was forced to hide her true identity and pass as White in order to leave a lasting legacy that enriched our nation, by New York Times bestselling authors Marie Benedict and Victoria Christopher Murray.
This book had my attention from the very first sentence, and I was so riveted that I listened to, and read, this book. The narrator of the Audible book, Robin Miles, is masterful as always. At the end of the audio book, the authors, Marie Benedict and Victoria Christopher Murray, each talked about the process of researching and writing this book, and how, as a result, they became close personal friends. This is a MUST read, so here is a little more about it:
In her twenties, Belle da Costa Greene is hired by J. P. Morgan to curate a collection of rare manuscripts, books, and artwork for his newly built Pierpont Morgan Library. Belle becomes a fixture in New York City society and one of the most powerful people in the art and book world, known for her impeccable taste and shrewd negotiating for critical works as she helps create a world-class collection.
But Belle has a secret, one she must protect at all costs. She was born not Belle da Costa Greene but Belle Marion Greener. She is the daughter of Richard Greener, the first Black graduate of Harvard and a well-known advocate for equality. Belle’s complexion isn’t dark because of her alleged Portuguese heritage that lets her pass as White—her complexion is dark because she is African American.
The Personal Librarian tells the story of an extraordinary woman, famous for her intellect, style, and wit, and shares the lengths she must go to—for the protection of her family and her legacy—to preserve her carefully crafted White identity in the racist world in which she lives. (Audible)
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for September and October, 2022. Included are reports from the Nebraska Department of Environment and Energy, the Nebraska Emergency Management Agency, the Nebraska Civil Defence Agency, the Nebraska Department Transportation, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
Book Briefs: New University of Nebraska Press Books at the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse
The Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse receives documents every month from all Nebraska state agencies, including the University of Nebraska Press (UNP). Each month we will be showcasing the UNP books that the Clearinghouse has received.
UNP books, as well as all Nebraska state documents, are available for checkout by libraries and librarians for their patrons.
Here are the UNP books the Clearinghouse received in September and October, 2022:
An Evolving Vision : The James Collection, 1997-2022, by Carolyn Ducey, Marin F. Hanson, and Penny McMorris.
In 2022 the International Quilt Museum (IQM) at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln celebrates a quarter century of studying, preserving, and exhibiting the Ardis and Robert James Collection. The Jameses’ donation of their unparalleled one-thousand-piece collection in 1997 established the IQM and formed the solid base from which the museum has steadily grown. Today, the museum’s collection includes more than six thousand quilts from five different centuries and over fifty countries, an expansion that has been encouraged by the James family, who continue to support the museum’s efforts to represent global quiltmaking.
This companion publication to the exhibition An Evolving Vision, 1997–2022 highlights important pieces from various segments of the collection: Classics—stunning antique American quilts; From the Studio—early and innovative art pieces; and New Horizons—quilt traditions from around the world. This book also includes a comprehensive catalog of the James Collection, comprising the quilts from the original 1997 gift as well as important groups given to the IQM in 2006 and 2009. An Evolving Vision documents the significance of the James Collection and underscores the broad vision its collectors developed not only for themselves but for the museum they so vitally helped shape.
The Enlightened Patrolman : Early Law Enforcement in Mexico City, by Nicole von Germeten; Series: Confluencias
When late eighteenth-century New Spanish viceregal administrators installed public lamps in the streets of central Mexico City, they illuminated the bodies of Indigenous, Afro-descended, and plebeian Spanish urbanites. The urban patrolmen, known as guarda faroleros, or “lantern guards,” maintained the streetlamps and attempted to clear the streets of plebeian sexuality, embodiment, and sociability, all while enforcing late colonial racial policies amid frequent violent resistance from the populace.
In The Enlightened Patrolman Nicole von Germeten guides readers through Mexico City’s efforts to envision and impose modern values as viewed through the lens of early law enforcement, an accelerated process of racialization of urban populations, and burgeoning ideas of modern masculinity. Germeten unfolds a tale of the losing struggle for elite control of the city streets. As surveillance increased and the populace resisted violently, a pause in the march toward modernity ensued. The Enlightened Patrolman presents an innovative study on the history of this very early law enforcement corps, providing new insight into the history of masculinity and race in Mexico, as well as the eighteenth-century origins of policing in the Americas.
Imperial Zions : Religion, Race, and Family in the American West and the Pacific, by Amanda Hendrix-Komoto; Series: Studies in Pacific Worlds
In the nineteenth century, white Americans contrasted the perceived purity of white, middle-class women with the perceived eroticism of women of color and the working classes. The Latter-day Saint practice of polygamy challenged this separation, encouraging white women to participate in an institution that many people associated with the streets of Calcutta or Turkish palaces. At the same time, Latter-day Saints participated in American settler colonialism. After their expulsion from Ohio, Missouri, and Illinois, Latter-day Saints dispossessed Ute and Shoshone communities in an attempt to build their American Zion. Their missionary work abroad also helped to solidify American influence in the Pacific Islands as the church became a participant in American expansion.
Imperial Zions explores the importance of the body in Latter-day Saint theology with the faith’s attempts to spread its gospel as a “civilizing” force in the American West and the Pacific. By highlighting the intertwining of Latter-day Saint theology and American ideas about race, sexuality, and the nature of colonialism, Imperial Zions argues that Latter-day Saints created their understandings of polygamy at the same time they tried to change the domestic practices of Native Americans and other Indigenous peoples. Amanda Hendrix-Komoto tracks the work of missionaries as they moved through different imperial spaces to analyze the experiences of the American Indians and Native Hawaiians who became a part of white Latter-day Saint families. Imperial Zions is a foundational contribution that places Latter-day Saint discourses about race and peoplehood in the context of its ideas about sexuality, gender, and the family.
Living Room, by Laura Bylenok; Series: The Backwaters Prize in Poetry
Deeply phenomenological and ecological, Laura Bylenok’s poems in Living Room imagine the lived reality of other organisms and kinds of life, including animals, plants, bacteria, buildings, and rocks. They explore the permeability of human and nonhuman experience, intelligence, language, and subjectivity. In particular, the poems consider so-called model organisms—nonhuman species studied to understand specific and often human biological processes, diseases, and phenomena—as well as an experience of self and world that cannot be objectively quantified. The impulse of these poems is to slow down, to see and feel, and to listen closely. Language becomes solid, palpable as fruit. Long lines propel breath and push past the lung’s capacity.
Life at a cellular level, synthesis and symbiosis, is revealed through forests, fairy tales, and vines that grow over abandoned houses and hospital rooms. A living room is considered as a room that is lived in and also a room that is alive. Cells are living rooms. A self is a room that shares walls with others. Interconnection and interplay are thematic, and the network of poems becomes a linguistic rendering of a heterogeneous and nonhierarchical ecosystem, using the language of biology, genetics, and neurochemistry alongside fairy tale and dream to explore the interior spaces of grief, motherhood, mortality, and self.
Might Kindred, by Monica Gomery; Series: The Raz/Shumaker Prairie Schooner Book Prize in Poetry
The poems of Might Kindred wonder aloud: can we belong to one another, and “can a people belong to a dreaming machine?” Conjuring mountains and bodies of water, queer and immigrant poetics, beloveds both human and animal, Mónica Gomery explores the intimately personal and the possibility of a collective voice. Here anthems are sung and fall apart midsong. The speaker exchanges letters with her ancestors, is visited by a shadow sister, and interrogates what it means to make a home as a first-generation American.
Winner of the Raz/Shumaker Prairie Schooner Book Prize in Poetry, the poems in Might Kindred are rooted in the body and its cousins, seeking the possibility of kinship, “in case we might kindness, might ardor together.” Belonging and unbelonging are claimed as part of the same complicated whole, and Gomery’s intersections reach for something divine at the center.
Nez Perce Summer, 1877 : The U.S. Army and the Nee-Me-Poo Crisis, by Jerome A. Greene
Nez Perce Summer, 1877 tells the story of a people’s epic struggle to survive spiritually, culturally, and physically in the face of unrelenting military force. Written by one of the foremost experts in frontier military history, Jerome A. Greene, and reviewed by members of the Nez Perce tribe, this definitive treatment of the Nez Perce War is the first to incorporate research from all known accounts of Nez Perce and U.S. military participants.
Enhanced by sixteen detailed maps and forty-nine historic photographs, Greene’s gripping narrative takes readers on a three-and-one-half month 1,700-mile journey across the wilds of Idaho, Wyoming, and Montana territories. All of the skirmishes and battles of the war receive detailed treatment, which benefits from Greene’s astute analysis of the strategies and decision making on both sides.
Between 100 and 150 of the more than 800 Nez Perce men, women, and children who began the trek were killed during the war. Almost as many died in the months following the surrender, after they were exiled to malaria-ridden northeastern Oklahoma. Army deaths numbered 113. The casualties on both sides were an extraordinary price for a war that nobody wanted but whose history has since fascinated generations of Americans.
The North American West in the Twenty-First Century, edited by Brenden W. Rensink
In 1893 Frederick Jackson Turner famously argued that the generational process of meeting and conquering the supposedly uncivilized western frontier is what forged American identity. In the late twentieth century, “new western” historians dissected the mythologized western histories that Turner and others had long used to embody American triumph and progress. While Turner’s frontier is no more, the West continues to present America with challenging processes to wrestle, navigate, and overcome.
The North American West in the Twenty-First Century, edited by Brenden W. Rensink, takes stories of the late twentieth-century “modern West” and carefully pulls them toward the present—explicitly tracing continuity with or unexpected divergence from trajectories established in the 1980s and 1990s. Considering a broad range of topics, including environment, Indigenous peoples, geography, migration, and politics, these essays straddle multiple modern frontiers, not least of which is the temporal frontier between our unsettled past and uncertain future. These forays into the twenty-first-century West will inspire more scholars to pull histories to the present and by doing so reinsert scholarly findings into contemporary public awareness.
The Old Iron Road : An Epic of Rails, Roads, and the Urge to Go West, by David Haward Bain
In the summer of 2000 David Haward Bain and his family left their home in Vermont and headed west in search of America’s past. Spiritually, their journey began on a Kansas trail where the author’s grandmother was born in a covered wagon in 1889. Between the Missouri River and the Golden Gate, they retraced the entire route of the first transcontinental railroad and large stretches of the Oregon and California trails, and the equally colorful old Lincoln Highway. Following vanished iron rails and wagon wheel ruts, bumping down backroads and main streets, they discovered the deep, restless, uniquely American spirit of adventure that connects our past to our present.
A superb writer and an exacting researcher, Bain conjures up a marvelous sense of coming unstuck in time as he lingers in the ghost towns and battlegrounds, prairies and river ports, trainyards, museums, deserts, and diners that line his cruise west to California. Bain encounters a fascinating cast of characters, both historic and contemporary, as well as memories of his grandparents and the journeys that shaped his own heritage.
Writing in the tradition of William Least Heat-Moon and Ian Frazier, and with an engaging warmth and a deep grasp of history all his own, Bain has fashioned a quintessentially American journey.
Outback & Out West : The Settler-Colonial Environmental Imaginery, by Tom Lynch.
Outback and Out West examines the ecological consequences of a settler-colonial imaginary by comparing expressions of settler colonialism in the literature of the American West and Australian Outback. Tom Lynch traces exogenous domination in both regions, which resulted in many similar means of settlement, including pastoralism, homestead acts, afforestation efforts, and bioregional efforts at “belonging.” Lynch pairs the two nations’ texts to show how an analysis at the intersection of ecocriticism and settler colonialism requires a new canon that is responsive to the social, cultural, and ecological difficulties created by settlement in the West and Outback.
Outback and Out West draws out the regional Anthropocene dimensions of settler colonialism, considering such pressing environmental problems as habitat loss, groundwater depletion, and mass extinctions. Lynch studies the implications of our settlement heritage on history, art, and the environment through the cross-national comparison of spaces. He asserts that bringing an ecocritical awareness to settler-colonial theory is essential for reconciliation with dispossessed Indigenous populations as well as reparations for ecological damages as we work to decolonize engagement with and literature about these places.
Paternalism to Partnership : The Administration of Indian Affairs, 1786-2021, by David H. DeJong
Paternalism to Partnership examines the administration of Indian affairs from 1786, when the first federal administrator was appointed, through 2021. David H. DeJong examines each administrator through a biographical sketch and excerpts of policy statements defining the administrator’s political philosophy, drawn from official reports or the administrator’s own writings.
The Indian Office, as an executive agency under the secretary of war (1789 to 1849) and secretary of the interior (1849 to present), was directed by the president of the United States. The superintendents, chief clerks, commissioners, and assistant secretaries for Indian affairs administered policy as prescribed by Congress and the president. Each was also given a level of discretion in administering this policy. For most of the federal-Indian relationship, administrators were limited in influencing policy. This paternalism continued well into the twentieth century. Beginning in the 1960s Congress and the president ameliorated their views on the federal-Indian relationship and moved away from paternalism. Since 1966 every administrator of the Bureau of Indian Affairs has been Native American, and each has exercised increasing authority in shaping policy. This has given rise to a federal-Indian partnership that has witnessed tribal nations again exercising their inherent rights of self-government.
In this documentary history David H. DeJong follows the progression of federal Indian policy over more than two hundred years, providing firsthand accounts of how the federal-Indian relationship has changed over the centuries.
The Settler Sea : California’s Salton Sea and the Consequences of Colonialism, by Traci Brynne Voyles
2022 WHA Caughey Western History Prize for the most distinguished book on the American West
Can a sea be a settler? What if it is a sea that exists only in the form of incongruous, head-scratching contradictions: a wetland in a desert, a wildlife refuge that poisons birds, a body of water in which fish suffocate? Traci Brynne Voyles’s history of the Salton Sea examines how settler colonialism restructures physical environments in ways that further Indigenous dispossession, racial capitalism, and degradation of the natural world. In other words, The Settler Sea asks how settler colonialism entraps nature to do settlers’ work for them.
The Salton Sea, Southern California’s largest inland body of water, occupies the space between the lush agricultural farmland of the Imperial Valley and the austere desert called “America’s Sahara.” The sea sits near the boundary between the United States and Mexico and lies at the often-contested intersections of the sovereign lands of the Torres Martinez Desert Cahuilla and the state of California. Created in 1905, when overflow from the Colorado River combined with a poorly constructed irrigation system to cause the whole river to flow into the desert, this human-maintained body of water has been considered a looming environmental disaster.
The Salton Sea’s very precariousness—the way it sits uncomfortably between worlds, existing always in the interstices of human and natural influences, between desert and wetland, between the skyward pull of the sun and the constant inflow of polluted water—is both a symptom and symbol of the larger precariousness of settler relationships to the environment, in the West and beyond. Voyles provides an innovative exploration of the Salton Sea, looking to the ways the sea, its origins, and its role in human life have been vital to the people who call this region home.
Standing Bear’s Quest for Freedom : The First Civil Rights Victory for Native Americans, by Lawrence A. Dwyer
Chief Standing Bear of the Ponca Nation faced arrest for leaving the U.S. government’s reservation, without its permission, for the love of his son and his people. Standing Bear fought for his freedom not through armed resistance but with bold action, strong testimony, and heartfelt eloquence. He knew he and his people had suffered a great injustice.
Standing Bear wanted the right to live and die with his family on the beloved land of his Ponca ancestors, located within the Great Plains of Nebraska. In telling his story, Standing Bear’s Quest for Freedom relates an unprecedented civil rights victory for Native Americans: for the first time, in 1879, a federal court declared a Native American to be a “person”—a human being with the right to file an action for a redress of grievances in a federal court, like every other person in the United States.
Standing Bear’s victory in Standing Bear v. Crook began a national movement of reforming Native American rights—albeit a slow one. Because of the courage and leadership of Chief Standing Bear, the pervasive spirit of indifference of most Americans toward Native Americans was disrupted by this historic decision. America would never be the same.
Strength From the Waters : A History of Indigenous Mobilization in Northwest Mexico, by James V. Mestaz
Strength from the Waters is an environmental and social history that frames economic development, environmental concerns, and Indigenous mobilization within the context of a timeless issue: access to water. Between 1927 and 1970 the Mayo people—an Indigenous group in northwestern Mexico—confronted changing access to the largest freshwater source in the region, the Fuerte River.
In Strength from the Waters James V. Mestaz demonstrates how the Mayo people used newly available opportunities such as irrigation laws, land reform, and cooperatives to maintain their connection to their river system and protect their Indigenous identity. By using irrigation technologies to increase crop production and protect lands from outsiders trying to claim it as fallow, the Mayo of northern Sinaloa simultaneously preserved their identity by continuing to conduct traditional religious rituals that paid homage to the Fuerte River. This shift in approach to both new technologies and natural resources promoted their physical and cultural survival and ensured a reciprocal connection to the Fuerte River, which bound them together as Mayo.
Mestaz examines this changing link between hydraulic technology and Mayo tradition to reconsider the importance of water in relation to the state’s control of the river and the ways the natural landscape transformed relations between individuals and the state, altering the social, political, ecological, and ethnic dynamics within several Indigenous villages. Strength from the Waters significantly contributes to contemporary Mexicanist scholarship by using an environmental and ethnohistorical approach to water access, Indigenous identity, and natural resource management to interrogate Mexican modernity in the twentieth century.
There Where It’s So Bright in Me, by Tanella Boni; Series: African Poetry Book
There Where It’s So Bright in Me pries at the complexities of difference—race, religion, gender, nationality—that shape twenty-first-century geopolitical conditions. With work spanning more than thirty-five years and as one of the most prominent figures in contemporary African literature, Tanella Boni is uniquely positioned to test the distinctions of self, other, and belonging. Two twenty-first-century civil wars have made her West African home country of Côte d’Ivoire unstable. Abroad in the United States, Boni confronts the racialized violence that accompanies the idea of Blackness; in France, a second home since her university days, Boni encounters the nationalism roiling much of Europe as the consequences of (neo)colonialism shift the continent’s ethnic and racial profile.
What would it mean for the borders that segregate—for these social, political, cultural, personal, and historicizing forces that enshroud us—to lose their dominion? In a body under constant threat, how does the human spirit stay afloat? Boni’s poetry is characterized by a hard-earned buoyancy, given her subject matter. Her empathy, insight, and plainspoken address are crucial contributions to the many difficult contemporary conversations we must engage.
**Pictures and Synopses courtesy of University of Nebraska Press.
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for July and August 2022. Included are reports from the Nebraska Auditor of Public Accounts, the Nebraska Board of Examiners, the Nebraska Department of Education, the Nebraska Department Transportation, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
Book Briefs: New University of Nebraska Press Books at the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse
The Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse receives documents every month from all Nebraska state agencies, including the University of Nebraska Press (UNP). Each month we will be showcasing the UNP books that the Clearinghouse has received.
UNP books, as well as all Nebraska state documents, are available for checkout by libraries and librarians for their patrons.
Here are the UNP books the Clearinghouse received in July and August, 2022:
Journey into Christmas, and, Star Across the Tracks, by Bess Streeter Aldrich.
The true meaning of Christmas emerges in Bess Streeter Aldrich’s two enchanting stories about reunited families, good fellowship, and restored faith. The head may tell the heart all sorts of things, but at Christmastime the heart is stronger, so take a journey back through Christmases when something quite ordinary turns out to be miraculous. Both heartfelt and genuine, the stories “Journey into Christmas” and “Star across the Tracks” remind us to cherish the holidays with those we love, the ways we grow, and the memories we make throughout life.
Mummy Eaters, by Sherry Shenoda ; Series: African Poetry Book
Winner of the Sillerman First Book Prize for African Poets, Sherry Shenoda’s collection Mummy Eaters follows in the footsteps of an imagined ancestor, one of the daughters of the house of Akhenaten in the Eighteenth Dynasty, Egypt. Shenoda forges an imagined path through her ancestor’s mummification and journey to the afterlife. Parallel to this exploration run the implications of colonialism on her passage.
The mythology of the ancient Egyptians was oriented toward resurrection through the preservation of the human body in mummification. Shenoda juxtaposes this reverence for the human body as sacred matter and a pathway to eternal life with the sixteenth- and seventeenth-century European fascination with ingesting Egyptian human remains as medicine and using exhumed Egyptian mummies as paper, paint, and fertilizer. Today Egyptian human remains are displayed in museums. Much of Mummy Eaters is written as a call and response, in the Coptic tradition, between the imagined ancestor and the author as descendant.
If This Were Fiction : A Love Story in Essays, by Jill Christman ; Series: American Lives
If This Were Fiction is a love story—for Jill Christman’s long-ago fiancé, who died young in a car accident; for her children; for her husband, Mark; and ultimately, for herself. In this collection, Christman takes on the wide range of situations and landscapes she encountered on her journey from wild child through wounded teen to mother, teacher, writer, and wife. In these pages there are fatal accidents and miraculous births; a grief pilgrimage that takes Christman to jungles, volcanoes, and caves in Central America; and meditations on everything from sexual trauma and the more benign accidents of childhood to gun violence, indoor cycling, unlikely romance, and even a ghost or two.
Playing like a lively mixtape in both subject and style, If This Were Fiction focuses an open-hearted, frequently funny, clear-eyed feminist lens on Christman’s first fifty years and sends out a message of love, power, and hope.
Vanished : Stories, by Karin Lin-Greenberg ; Series: The Raz/Shumaker Prairie Schooner Book Prize in Fiction
Winner of the Raz/Shumaker Prairie Schooner Book Prize in Fiction, Vanished tells the stories of women and girls in upstate New York who are often overlooked or unseen by the people around them. The characters range from an aging art professor whose students are uninterested in learning what she has to teach, to a young girl who becomes the victim of a cruel prank in a swimming pool, to a television producer who regrets allowing her coworkers into her mother’s bird-filled house to film a show about animal hoarding because it will reveal too much about her family and past.
Humorous and empathetic, the collection exposes the adversity in each character’s life; each deals with something or someone who has vanished—a person close to her, a friendship, a relationship—as she seeks to make sense of the world around her in the wake of that loss.
Under My Bed and Other Essays, by Jody Keisner ; Series: American Lives
Jody Keisner was raised in rural Nebraska towns by a volatile father and kind but passive mother. As a young adult living alone for the first time, she began a nighttime ritual of checking under her bed each night, not sure who she was afraid of finding. An intruder? A monster? Her father? Keisner’s fears mature as she becomes a wife and mother, and the boogeyman under the bed shape-shifts, though its shapes are no less frightening—a young aunt’s drowning, the “chest chomp” in the classic horror movie The Thing, a diagnosis of a chronic autoimmune disease, the murder of a young college student, an eccentric grandmother’s belief in reincarnation and her dying advice: “Don’t be afraid.”
In Under My Bed and Other Essays, Jody Keisner searches for the roots of the violence and fear that afflict women, starting with the working-class midwestern family she was adopted into and ending with her own experience of mothering daughters. In essays both literary and experimental, Keisner illustrates the tension between the illusion of safety, our desire for control, and our struggle to keep the things we fear from reaching out and pulling us under.
Cotton Candy : Poems Dipped Out of the Air, by Ted Kooser
“Poems dipped out of the air” describes the manner in which Ted Kooser composed the poems in Cotton Candy, the result of his daily routine of getting up long before dawn, sitting with coffee, pen, and notebook, and writing whatever drifts into his mind. Whether those words and images are serious or just plain silly, Kooser tries not to censor himself. His objective is to catch whatever comes to him, to snatch it out of the air in words, rhythms, and cadences, the way a cotton candy vendor dips an airy puff out of a cloud of spun sugar and hands it to his customer. Poems written in fun and now shared with the reader, Kooser’s playful and magical confections charm and delight.
**Pictures and Synopses courtesy of University of Nebraska Press.
Friday Reads: Before We Were Yours, by Lisa Wingate
I’ll be honest right off the bat here–I resisted reading this book for a very long time–almost 5 years to be exact. Even though it’s been very popular, as an adoptee, I tend to shy away from stories about adoption. Not because my own adoption was bad, but because I’ve heard stories and know some adoptees personally, whose lives did not turn out as well as mine.
That being said, Before We Were Yours, by Lisa Wingate, is powerful, well-written, and based on one of America’s most notorious real-life adoption scandals. It is a story of families torn apart, but sometimes, in the end, brought together again.
Memphis, 1939. Twelve-year-old Rill Foss and her four younger siblings live a magical life aboard their family’s Mississippi River shantyboat. But when their father must rush their mother to the hospital one stormy night, Rill is left in charge – until strangers arrive in force. Wrenched from all that is familiar and thrown into a Tennessee Children’s Home Society orphanage, the Foss children are assured that they will soon be returned to their parents – but they quickly realize the dark truth. At the mercy of the facility’s cruel director, Rill fights to keep her sisters and brother together in a world of danger and uncertainty.
Aiken, South Carolina, present day. Born into wealth and privilege, Avery Stafford seems to have it all: a successful career as a federal prosecutor, a handsome fiancé, and a lavish wedding on the horizon. But when Avery returns home to help her father weather a health crisis, a chance encounter leaves her with uncomfortable questions and compels her to take a journey through her family’s long-hidden history, on a path that will ultimately lead either to devastation or to redemption.
Lisa Wingate’s riveting, wrenching, and ultimately uplifting tale reminds us how, even though the paths we take can lead to many places, the heart never forgets where we belong. Amazon.com
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for May and June 2022. Included are reports from the Nebraska Foster Care Review Office, the Nebraska State Patrol, the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services, the Nebraska Judicial Branch, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
Book Briefs: New University of Nebraska Press Books at the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse
The Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse receives documents every month from all Nebraska state agencies, including the University of Nebraska Press (UNP). Each month we will be showcasing the UNP books that the Clearinghouse has received.
UNP books, as well as all Nebraska state documents, are available for checkout by libraries and librarians for their patrons.
Here are the UNP books the Clearinghouse received in May and June, 2022:

A Frail Liberty : Probationary Citizens in the French and Haitian Revolutions, by Tessie P. Liu ; Series: France Overseas: Studies in Empire and Decolonization
A Frail Liberty traces the paradoxical actions of the first French abolitionist society, the Société des Amis des Noirs (Society of the Friends of Blacks), at the juncture of two unprecedented achievements of the revolutionary era: the extension of full rights of citizenship to qualifying free men of color in 1792 and the emancipation decree of 1794 that simultaneously declared the formerly enslaved to be citizens of France. This society helped form the revolution’s notion of color-blind equality yet did not protest the pro-slavery attack on the new citizens of France. Tessie P. Liu prioritizes the understanding of the elite insiders’ vision of equality as crucial to understanding this dualism.
By documenting the link between outright exclusion and political inclusion and emphasizing that a nation’s perceived qualifications for citizenship formulate a particular conception of racial equality, Liu argues that the treatment and status distinctions between free people of color and the formerly enslaved parallel the infamous divide between “active” and “passive” citizens. These two populations of colonial citizens with African ancestry then must be considered part of the normative operations of French citizenship at the time. Uniquely locating racial differentiation in the French and Haitian revolutions within the logic and structures of political representation, Liu deepens the conversation regarding race as a civic identity within democratic societies.

A Woman of Adventure : The Life and Times of First Lady Lou Henry Hoover, by Annette B. Dunlap.
When Lou Henry married Herbert Hoover in February 1899, she looked forward to a partnership of equality and a life of adventure. She could fire a rifle and sit a horse as well as any man. The Quaker community of Whittier, California, where she lived as a teen, reinforced the egalitarian spirit of her upbringing. But history had other ideas for Lou Henry Hoover.
For the first fifteen years of married life, Lou globe-trotted with her husband as he pursued a lucrative career in mining engineering and consulting. World War I not only changed the map of the world, it changed the map of the Hoovers’ marriage. Herbert Hoover’s Commission for the Relief of Belgium launched him into a political career that led to the White House. Lou, who detested the limelight, led a dual life: she supported her husband’s political career, managed their multiple households, and saw to the needs of their family. Behind the scenes, she pursued her own interests.
History has long since forgotten the breadth of her achievements, but Lou Henry Hoover’s powerful legacy endures in the ongoing success of the Girl Scouts, the music and physical therapy degree programs at Stanford University, athletic opportunities for women, and the countless unknown men and women who received an education thanks to Lou’s anonymous financial support.
Conveying Lou’s humor, personality, and intelligence, A Woman of Adventure takes a fresh look at the first lady who preceded Eleanor Roosevelt and her also-extraordinary accomplishments.

Cattle Beet Capital : Making Industrial Agriculture in Northern Colorado, by Michael Weeks.
In 1870 several hundred settlers arrived at a patch of land at the confluence of the South Platte and Cache la Poudre Rivers in Colorado Territory. Their planned agricultural community, which they named Greeley, was centered around small landholdings, shared irrigation, and a variety of market crops. One hundred years later, Greeley was the home of the world’s largest concentrated cattle-feeding operation, with the resources of an entire region directed toward manufacturing beef. How did that transformation happen? Cattle Beet Capital is animated by that question.
Expanding outward from Greeley to all of northern Colorado, Cattle Beet Capital shows how the beet sugar industry came to dominate the region in the early twentieth century through a reciprocal relationship with its growers that supported a healthy and sustainable agriculture while simultaneously exploiting tens of thousands of migrant laborers. Michael Weeks shows how the state provided much of the scaffolding for the industry in the form of tariffs and research that synchronized with the agendas of industry and large farmers. The transformations that led to commercial feedlots began during the 1930s as farmers replaced crop rotations and seasonal livestock operations with densely packed cattle pens, mono-cropped corn, and the products pouring out of agro-industrial labs and factories. Using the lens of the northern Colorado region, Cattle Beet Capital illuminates the historical processes that made our modern food systems.

Creek Internationalism in an Age of Revolution, 1763–1818, by James L. Hill ; Series: Borderlands and Transcultural Studies
Creek Internationalism in an Age of Revolution, 1763–1818 examines how Creek communities and their leaders remained viable geopolitical actors in the trans-Appalachian West well after the American Revolution. The Creeks pursued aggressive and far-reaching diplomacy between 1763 and 1818 to assert their territorial and political sovereignty while thwarting American efforts to establish control over the region. The United States and the Creeks fought to secure recognition from the powers of Europe that would guarantee political and territorial sovereignty: the Creeks fought to maintain their connections to the Atlantic world and preserve their central role in the geopolitics of the trans-Appalachian West, while the American colonies sought first to establish themselves as an independent nation, then to expand borders to secure diplomatic and commercial rights.
Creeks continued to forge useful ties with agents of European empires despite American attempts to circumscribe Creek contact with the outside world. The Creeks’ solicitation of trade and diplomatic channels with British and Spanish colonists in the West Indies, Canada, and various Gulf Coast outposts served key functions for defenders of local autonomy. Native peoples fought to preserve the geopolitical order that dominated the colonial era, making the trans-Appalachian West a kaleidoscope of sovereign peoples where negotiation prevailed. As a result, the United States lacked the ability to impose its will on its Indigenous neighbors, much like the European empires that had preceded them. Hill provides a significant revisionist history of Creek diplomacy and power that fills gaps within the broader study of the Atlantic world and early American history to show how Indigenous power thwarted European empires in North America.

Dirt Persuasion : Civic Environmental Populism and Heartland’s Pipeline Fight, by Derek Moscato.
Dirt Persuasion examines a watershed moment in U.S. environmental politics: the fight over the Keystone XL Pipeline. The complex interplay of resources extraction industries with grassroots environmentalism and advocacy has transformed the role of activists in the contemporary public sphere. Bold Nebraska’s years-long fight against pipeline company TransCanada provides a compelling case study: a contemporary state-level organization that simultaneously challenged political and business leaders in its home state of Nebraska, at the national level in the United States, and in the foreign jurisdiction of Canada.
Dirt Persuasion sheds light not only on the activism practices of social movements but also on the changing environments in which such actions are deployed. The KXL Pipeline fight represents a watershed moment both for U.S. energy politics and in the communication of environmental activism. The rural dimension of this environmental saga is critical: environmentalism must be understood from the perspective of the rural Americans who coexist with one of the planet’s most delicate ecologies. Populism, rhetorical appeals, strategic advocacy framing, and media framing all factor prominently within the pipeline debate—leading to a civic environmental persuasion built on the attributes of narrative, engagement, hyperlocalization, and bipartisanship in order to build broad stakeholder support and influence public policy.

Eye on the World : A Life in International Service, by Anthony C. E. Quainton.
Eye on the World is the autobiography of diplomat Anthony C. E. Quainton, the story of a long and varied life lived in eleven countries on six continents. Rather than a formal history, this is Quainton’s reflection on his interactions with the events of those times, beginning with George VI’s historic visit to North America in 1939, through the years of the Cold War, the efforts to contain and then defeat the Soviet Union, and finally the two decades of uneasy peace that came after the fall of the Berlin Wall. To some of these events Quainton was merely a spectator. In other areas—India, Nicaragua, Kuwait, and Peru—he was actively involved either as a participant in the policy process in Washington or as the senior representative of the United States in those countries.
Spanning his upbringing and education through two decades after his retirement, Quainton describes the expanding horizons of a middle-class boy from the northwest corner of North America as he encountered the complexity of the world in which he spent his professional life. Quainton served in seven different presidential appointments under presidents Gerald Ford, Jimmy Carter, Ronald Reagan, George H. W. Bush, and Bill Clinton. These included four ambassadorships in distinct parts of the world and three assistant secretary–level posts in Washington. This range of geographic and functional assignments was unique in his generation of Foreign Service officers.

In Praise of the Ancestors : Names, Identity, and Memory in Africa and the Americas, by Susan Elizabeth Ramirez ; Series: Borderlands and Transcultural Studies
Apart from collective memories of lived experiences, much of the modern world’s historical sense comes from written sources stored in the archives of the world, and some scholars in the not-so-distant past have described unlettered civilizations as “peoples without history.” In Praise of the Ancestors is a revisionist interpretation of early colonial accounts that reveal incongruities in accepted knowledge about three Native groups.
Susan Elizabeth Ramírez reevaluates three case studies of oral traditions using positional inheritance—a system in which names and titles are inherited from one generation by another and thereby contribute to the formation of collective memories and a group identity. Ramírez begins by examining positional inheritance and perpetual kinship among the Kazembes in central Africa from the eighteenth to the mid-twentieth centuries. Next, her analysis moves to the Native groups of the Iroquois Confederation and their practice of using names to memorialize remarkable leaders in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Finally, Ramírez surveys naming practices of the Andeans, based on sixteenth-century manuscript sources and later testimonies found in Spanish and Andean archives, questioning colonial narratives by documenting the use of this alternative system of memory perpetuation, which was initially unrecognized by the Spaniards.
In the process of reexamining the histories of Native peoples on three continents, Ramírez broaches a wider issue: namely, understanding of the nature of knowledge as fundamental to understanding and evaluating the knowledge itself.

The Great Plains, 2nd ed., by Walter Prescott Webb.
This iconic description of the interaction between the vast central plains of the continent and the white Americans who moved there in the mid-nineteenth century has endured as one of the most influential, widely known, and controversial works in western history since its first publication in 1931. Arguing that “the Great Plains environment . . . constitutes a geographic unity whose influences have been so powerful as to put a characteristic mark upon everything that survives within its borders,” Walter Prescott Webb identifies the revolver, barbed wire, and the windmill as technological adaptations that facilitated Anglo conquest of the arid, treeless region. Webb draws on history, anthropology, geography, demographics, climatology, and economics in arguing that the 98th Meridian constitutes an institutional fault line at which “practically every institution that was carried across it was either broken and remade or else greatly altered.”
This new edition of one of the foundational works of western American history features an introduction by Great Plains historian Andrew R. Graybill and a new index and updated design.

Under Prairie Skies : The Plants and Native Peoples of the Northern Plains, by C. Thomas Shay.
In Under Prairie Skies, C. Thomas Shay asks and answers the question, What role did plants play in the lives of early inhabitants of the northern Great Plains? Since humans arrived at the end of the Ice Age, plants played important roles as Native peoples learned which were valuable foods, which held medicinal value, and which were best for crafts.
Incorporating Native voices, ethnobotanical studies, personal stories, and research techniques, Under Prairie Skies shows how, since the end of the Ice Age, plants have held a central place in the lives of Native peoples. Eventually some groups cultivated seed-bearing annuals and, later, fields of maize and other crops. Throughout history, their lives became linked with the land, both materially and spiritually.
**Pictures and Synopses courtesy of University of Nebraska Press.
Get Internet : The Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP)
Learn how President Biden is reducing the cost of high-speed internet and find out if you qualify to sign up.
As part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, President Biden and Vice President Harris worked with Democrats, Republicans, and Independents to create the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), which provides eligible households $30 per month off their internet bills. To deliver maximum cost savings to families, the Biden-Harris Administration has secured commitments from 20 leading internet providers to offer ACP-eligible households a high-speed internet plan for no more than $30 per month. Eligible families who pair their ACP benefit with one of these plans can receive high-speed internet at no cost.
Find Out If You Qualify
There are three different ways to qualify for the ACP benefit. You are eligible if you meet any one of the three qualifications below:
- Your income is at or below 200% of the Federal Poverty Guidelines (see chart below)
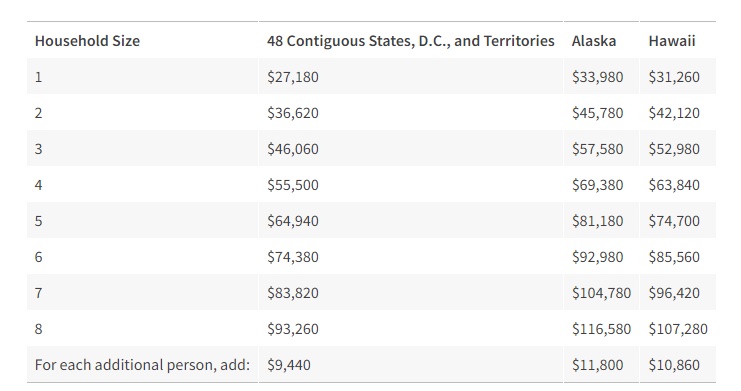
- You or someone in your household participates in one of these other programs:
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as Food Stamps
- Medicaid
- Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
- Federal Public Housing Assistance (FPHA)
- Veterans Pension and Survivors Benefit
- Free and Reduced-Price School Lunch Program or School Breakfast Program, including at U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Community Eligibility Provision schools
- Federal Pell Grant (received in the current award year)
- Lifeline
- Certain Tribal assistance programs, including Bureau of Indian Affairs General Assistance, Head Start (only households meeting the income qualifying standard), Tribal Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (Tribal TANF), and Food Distribution Program on Indian Reservations
- You meet the eligibility criteria for a participating broadband provider’s existing low-income internet program.
How To Sign Up for the Affordable Connectivity Program
Step 1: Claim Your Affordable Connectivity Program Benefit.
- You can send in an application by mail:
- You can sign up through your existing internet service provider if it participates in the program. Participating companies may ask you to apply through their company’s own application process.
Step 2: Contact a participating internet service provider to choose an internet plan.
- Once your application is approved, contact a participating internet service provider to choose a plan and apply your benefit to that plan.
- More information on how to apply can be found at https://acpbenefit.org/how-to-apply/ or by calling (877) 384-2575.
Participating Service Providers
These internet service providers offer a high-speed internet plan for $30 per month or less. If you apply your ACP benefit to one of these plans, you will have no out-of-pocket cost for internet.
- Allo Communications
- AltaFiber (and Hawaiian Telecom)
- Altice (Optimum and Suddenlink)
- Astound
- AT&T
- Breezeline
- Comcast
- Comporium
- Cox Communications
- Frontier
- IdeaTek
- Jackson Energy Authority
- Mediacom
- MLGC
- Spectrum (Charter Communications)
- Starry
- Verizon (Fios only)
- Vermont Telephone Company
- Vexus Fiber
- Wow! Internet, Cable and TV
You can also choose to apply your ACP benefit to a different provider. There are over 1,300 providers that accept the ACP benefit. To find one near you, visit https://acpbenefit.org/companies-near-me/.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What if I also need help getting a tablet or computer?
ACP-eligible households can also receive a one-time discount of up to $100 to purchase a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet from certain participating providers, with a small copay. To get a discounted device, contact a participating provider. The providers offering discounted devices are listed at https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program-providers
How much is my Affordable Connectivity Program benefit?
Most eligible families can receive a benefit of up to $30 per month applied to the cost of their internet service. ACP-eligible households who live on Tribal lands are eligible for a benefit of up to $75 per month.
Are these plans fast?
Yes – they offer a minimum of 100 Mbps download speed, which is fast enough for a typical family of 4 to video conference, stream movies or TV, and more.
What’s Up Doc? New State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

New state agency publications have been received at the Nebraska Library Commission for April 2022. Included are reports from the Nebraska Legislature, the Nebraska Department of Natural Resources, the Nebraska Department of Correctional Services, the Nebraska Department of Transportation, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.
What’s Up Doc? 2021 State Agency Publications at the Nebraska Library Commission

State agency publications received at the Nebraska Library Commission for 2021 are listed below. Included are reports from the Nebraska Department of Agriculture, the Nebraska Department of Economic Development, the Nebraska Department of Education, the Nebraska Game & Parks Commission, and new books from the University of Nebraska Press, to name a few.
Most items, except the books from the University of Nebraska Press, are available for immediate viewing and printing by clicking on the highlighted link above, or directly in the .pdf below. You can read synopses of the books received from the University of Nebraska Press in the Book Briefs blogposts.
The Nebraska Legislature created the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse in 1972 as a service of the Nebraska Library Commission. Its purpose is to collect, preserve, and provide access to all public information published by Nebraska state agencies. By law (State Statutes 51-411 to 51-413) all Nebraska state agencies are required to submit their published documents to the Clearinghouse. For more information, visit the Nebraska Publications Clearinghouse page, contact Mary Sauers, Government Information Services Librarian; or contact Bonnie Henzel, State Documents Staff Assistant.






































































